The Hidden Science Behind Parrots’ Vibrant Colors
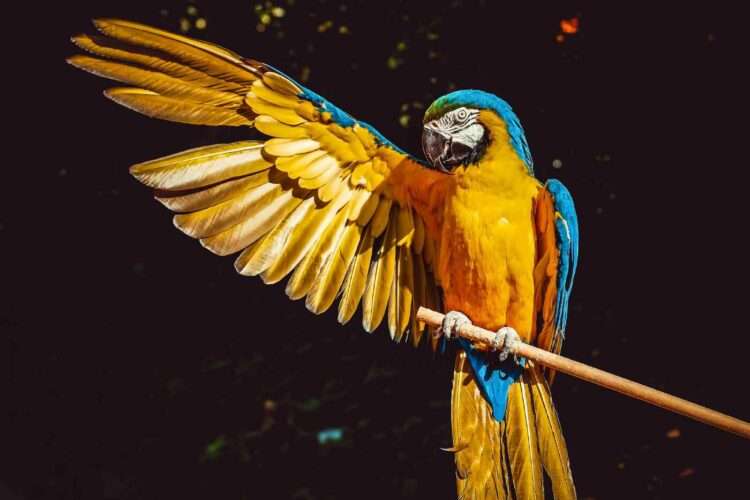
Parrots are known for their dazzling array of colors, from brilliant reds and oranges to vivid greens and blues. But what exactly makes these birds so colorful? Scientists have been investigating the molecular mechanisms that produce these vibrant hues, focusing on special pigments and the genes that control them.
Understanding Parrot Pigments
The colors in parrot feathers come from a combination of pigments and structural features. The primary pigments responsible are called psittacofulvins. These are unique to parrots and produce red, yellow, and green colors in their feathers. According to the supplementary materials from a study by Roberto Arbore and colleagues, researchers assessed the presence of these pigments in all 354 parrot species.
Yellow psittacofulvins appear in feathers that are yellow or green. The green color results from a combination of yellow pigments and blue structural coloration. Red psittacofulvins, on the other hand, are found in feathers that are red, pink, or orange. These pigments are more concentrated in certain species, giving them their distinctive bright red hues.
Investigating Feather Structure with Raman Spectroscopy
To delve deeper into how these pigments work, scientists used a technique called Raman spectroscopy. This method involves shining a laser on the feather and analyzing the light that scatters back. It helps identify the specific molecules present in the feathers without damaging them.
The study mentioned that intact feathers from various parrot species were examined. By comparing the spectra (the light patterns) from different colored feathers, researchers could see the unique signatures of psittacofulvin pigments. This non-invasive technique allowed them to understand better how different pigments contribute to the overall coloration of the feathers.
Genetic Insights: The Role of the ALDH3A2 Gene
Beyond pigments, genes play a crucial role in determining feather color. The researchers focused on a gene called ALDH3A2. They performed genome assembly and annotation for the dusky lory, a parrot species with notable color variations. By examining the DNA from these birds, they aimed to find genetic differences that might explain why some parrots are more colorful than others.
According to the study, they collected samples from both red and yellow dusky lories. By comparing the genomes, they looked for variations in the ALDH3A2 gene that correlated with the different colors. This gene is believed to be involved in the synthesis of pigments, and differences in its sequence might lead to variations in feather coloration.
Exploring Feather Development Through Transcriptomics
The researchers didn’t stop at genetics. They also looked at how genes are expressed in developing feathers using a technique called transcriptomics. This method involves sequencing RNA, which is like a snapshot of which genes are active at a given time.
By analyzing RNA from regenerating feather follicles of both red and yellow parrots, scientists could see which genes were turned on or off during feather growth. This information helps explain how genetic differences translate into physical characteristics like feather color.
From Birds to Yeast: Experimenting with Pigment Production
To test their findings, the scientists conducted experiments using yeast cells. They introduced the parrot genes responsible for pigment production into yeast to see if they could produce the same pigments. This approach allows researchers to study the function of specific genes in a controlled environment.
The yeast experiments confirmed that the ALDH3A2 gene plays a significant role in pigment production. When the gene was active, the yeast cells produced pigments similar to those found in parrot feathers. This result supports the idea that variations in this gene contribute to the bright colors seen in parrots.
Implications and Future Research
Understanding the molecular mechanisms behind parrot coloration has broader implications. It can help in conservation efforts by providing insights into how genetic diversity affects physical traits. It also adds to our knowledge of genetics, evolution, and how specific genes influence appearance.
Moreover, this research could inspire new technologies or materials that mimic the vibrant colors of parrot feathers. By learning from nature’s designs, scientists and engineers can develop novel applications in textiles, coatings, or displays.
Conclusion
Parrots’ bright colors are not just a feast for the eyes; they are the result of complex molecular processes involving unique pigments and specific genes like ALDH3A2. Through meticulous research combining spectroscopy, genetics, and experimental biology, scientists are uncovering the secrets behind these vibrant hues. This knowledge not only satisfies our curiosity but also opens doors to new scientific and technological advancements.
References:
- According to the supplementary materials by Roberto Arbore et al., “A molecular mechanism for bright color variation in parrots.”
- For more detailed scientific methods and findings, refer to the original study’s supplementary materials.